ABSTRACT
Since the publication of ICH Q9[1] in 2005, the pharmaceutical industry is encouraged to take a risk-based approach to the control and management of product quality. The expectation that Quality Risk Management (QRM) is integrated into the Pharmaceutical Quality System (PQS) is further developed in ICH Q10 [2]. ICH Q10 objectives are to achieve product realisation, to maintain a state of control, and to facilitate continuous improvement.
ICH Q10 states that the application of QRM can provide a proactive approach to identifying, scientifically evaluating, and controlling potential risks to quality. Most of the tools mentioned in ICH Q9, and commonly adopted by pharmaceutical companies, are focused on hazard identification and treatment. These treatments either improve the detection of the risk or reduce the likelihood of its occurrence. A treatment either serves to reposition the risk within a hierarchy or to a more acceptable ranking.
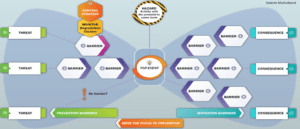
The tool proposed in this paper – The Bow Tie – transfers the focus to the treatments and places the emphasis on the identification and monitoring of prevention barriers, and mitigation barriers in operations environments. This approach develops a clear balance of prevention and mitigation in a risk control strategy.